×
- Hello
- Login or Register
- Quick Links
- Live Chat
- Track Order
- Parts Availability
- RMA
- Help Center
- Contact Us
- Shop for
- Hyundai Parts
- Hyundai Accessories


My Garage
My Account
Cart
Genuine Hyundai Sonata Catalytic Converter
Cat. Converter- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
34 Catalytic Converters found
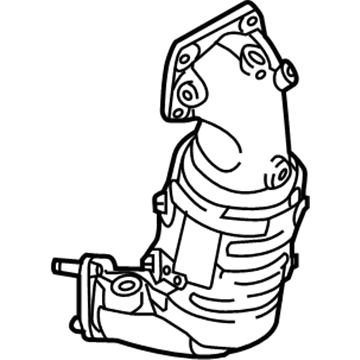
Hyundai Sonata Catalytic Converter Assembly
Part Number: 28950-2G420$1475.69 MSRP: $2110.06You Save: $634.37 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
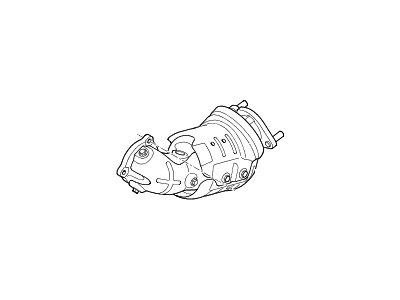
Hyundai Sonata Catalytic Converter Assembly
Part Number: 28950-25560$1834.93 MSRP: $2623.73You Save: $788.80 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Hyundai Sonata Catalytic Converter Assembly
Part Number: 28960-2G540$2346.77 MSRP: $3355.60You Save: $1008.83 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysHyundai Sonata Catalytic Converter Assembly
Part Number: 28950-3C300$1052.19 MSRP: $1504.50You Save: $452.31 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysHyundai Sonata Catalyst Case Assembly
Part Number: 28530-2GPA5$1043.06 MSRP: $1491.45You Save: $448.39 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysHyundai Sonata Catalyst Case Assembly
Part Number: 28530-2BLA0$2069.69 MSRP: $2959.40You Save: $889.71 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysHyundai Sonata Catalytic Converter Assembly
Part Number: 28950-2G310$1792.56 MSRP: $2563.15You Save: $770.59 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysHyundai Sonata Catalytic Converter Assembly
Part Number: 28950-32750$477.88 MSRP: $677.31You Save: $199.43 (30%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysHyundai Sonata Catalytic Converter Assembly
Part Number: 28950-32755$477.88 MSRP: $677.31You Save: $199.43 (30%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysHyundai Sonata Catalytic Converter Assembly
Part Number: 28950-32560$615.45 MSRP: $872.29You Save: $256.84 (30%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysHyundai Sonata Catalytic Converter Assembly
Part Number: 28950-32561$615.45 MSRP: $872.29You Save: $256.84 (30%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysHyundai Sonata Catalytic Converter Assembly
Part Number: 28950-32565$615.45 MSRP: $872.29You Save: $256.84 (30%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysHyundai Sonata Catalytic Converter Assembly
Part Number: 28950-32595$615.45 MSRP: $872.29You Save: $256.84 (30%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysHyundai Sonata Catalytic Converter Assembly
Part Number: 28950-32660$615.45 MSRP: $872.29You Save: $256.84 (30%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysHyundai Sonata Catalytic Converter Assembly
Part Number: 28950-32661$615.45 MSRP: $872.29You Save: $256.84 (30%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysHyundai Sonata Catalytic Converter Assembly
Part Number: 28950-32701$615.45 MSRP: $872.29You Save: $256.84 (30%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysHyundai Sonata Catalytic Converter Assembly
Part Number: 28950-32705$615.45 MSRP: $872.29You Save: $256.84 (30%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysHyundai Sonata Catalytic Converter Assembly
Part Number: 28950-33110$615.45 MSRP: $872.29You Save: $256.84 (30%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysHyundai Sonata Catalytic Converter Assembly
Part Number: 28950-33195$615.45 MSRP: $872.29You Save: $256.84 (30%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysHyundai Sonata Catalytic Converter Assembly
Part Number: 28950-33350$615.45 MSRP: $872.29You Save: $256.84 (30%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
| Page 1 of 2 |Next >
1-20 of 34 Results
Hyundai Sonata Catalytic Converter
If you are looking for affordable high-quality OEM Hyundai Sonata Catalytic Converter, then you have come to the prime place. Our website provides a large amount of genuine Hyundai Sonata Catalytic Converter at unbeatable prices. All our parts come backed with the manufacturer's warranty.
Hyundai Sonata Catalytic Converter Parts Questions & Experts Answers
- Q: What is the general description and replacement process for catalytic converters on Hyundai Sonata?A:Because of the federally mandated warranty coverage until five-years/60000 miles on emission-related components including the catalytic converter, it prudent to seek advice from dealer's service department before changing the converter at one's own cost. The catalytic converter is an emission control device in the exhaust system that reduces pollutants from exhaust gases, with two types: The oxidation catalyst decreases the hydrocarbons and the carbon monoxide by increasing the oxygen content to form water vapor and the carbon dioxide while the reduction catalyst minimizes the oxides of nitrogen by decreasing the oxygen content to form nitrogen and oxygen. These reagents are mixed together to form a three-way catalyst the that simultaneously deals with all three pollutants. The working of this catalyst is based on the input and consumption of oxygen; in case the catalyst is denied adequate oxygen, it cannot transform injurious emissions. This catalyst works best with the stoichiometric air-fuel ratio of 14.7:1, the variations from this can cause depletion of the element or excess affecting the performance of the catalyst. The Oxygen Sensor upstream and downstream report to the power train control module, in case the catalyst does not function properly it sets a diagnostic trouble code and turns on the CHECK ENGINE light. If a car owner believes that his/her vehicle's emission control system has malfunctioned, professional diagnosis and repair must be carried out by either a dealer or an authorized emissions inspection center. The extent of the damages, leaks and corrosion must be checked often especially if it is underbody parts that are being serviced. Despite being long lasting, catalytic converters can clog up and there is also what you can use to test for restricted vacuums within the exhaust system and this is the vacuum gauge. For replacement, the process changes from model to model; the aforesaid exhaust manifolds catalytic converters of 1999-2005 four-cylinder models are situated directly below the exhaust manifolds, the process includes; lifting the vehicle and ensuring it is steady, unbolting the exhaust pipe and disconnecting its rubber support, then, finally removing the converter. Other models, primary catalytic converters are integrated with the exhaust manifolds, the downstream is between the rear flange of the front exhaust pipe and the muffler which often time is replaced in muffler shops. In its stead, the vehicle needs to be lifted and supported as the converter needs to be quite literally pulled out through bolts and flanges.
Related Hyundai Sonata Parts
Browse by Year
2019 Catalytic Converter 2018 Catalytic Converter 2017 Catalytic Converter 2016 Catalytic Converter 2015 Catalytic Converter 2014 Catalytic Converter 2013 Catalytic Converter 2012 Catalytic Converter 2011 Catalytic Converter 2010 Catalytic Converter 2009 Catalytic Converter 2008 Catalytic Converter 2007 Catalytic Converter 2006 Catalytic Converter 2005 Catalytic Converter 2004 Catalytic Converter 2003 Catalytic Converter 2002 Catalytic Converter 2001 Catalytic Converter 2000 Catalytic Converter 1999 Catalytic Converter 1998 Catalytic Converter 1997 Catalytic Converter 1996 Catalytic Converter 1995 Catalytic Converter 1994 Catalytic Converter 1993 Catalytic Converter 1992 Catalytic Converter 1991 Catalytic Converter 1990 Catalytic Converter 1989 Catalytic Converter 1988 Catalytic Converter