×
- Hello
- Login or Register
- Quick Links
- Live Chat
- Track Order
- Parts Availability
- RMA
- Help Center
- Contact Us
- Shop for
- Hyundai Parts
- Hyundai Accessories


My Garage
My Account
Cart
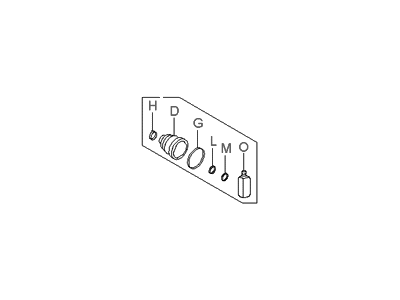
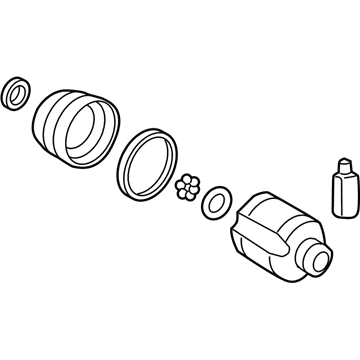
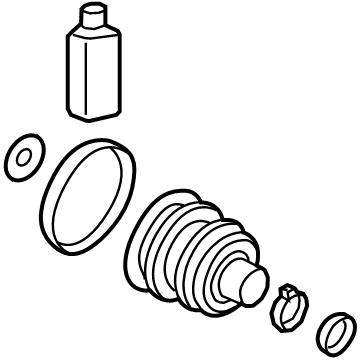
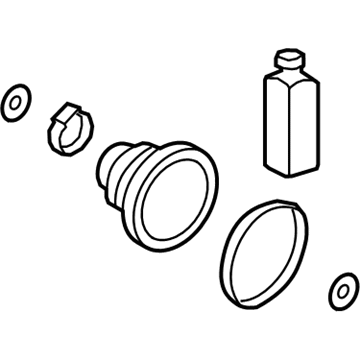
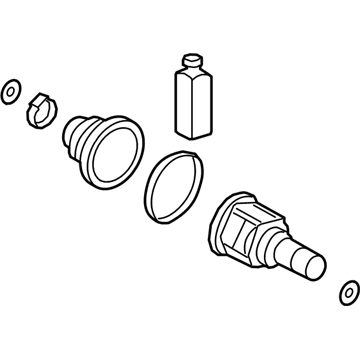
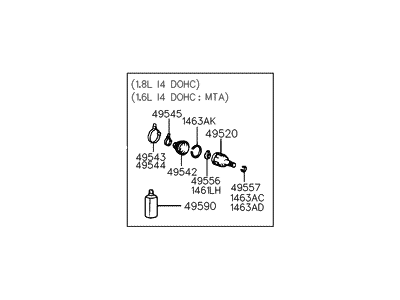
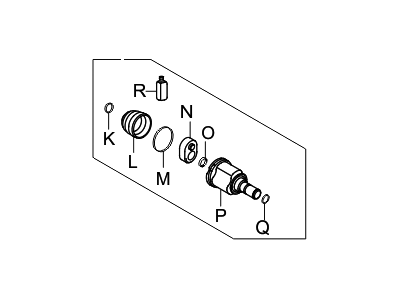
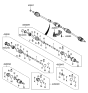
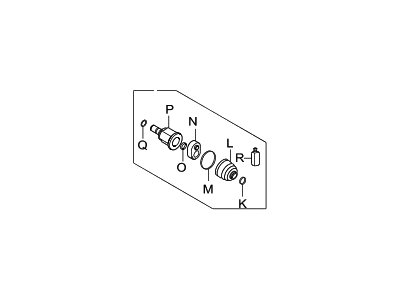
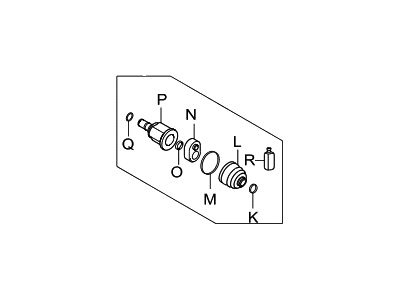
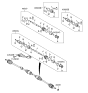
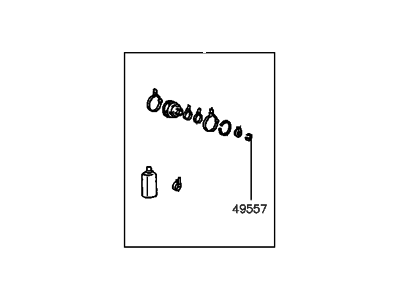
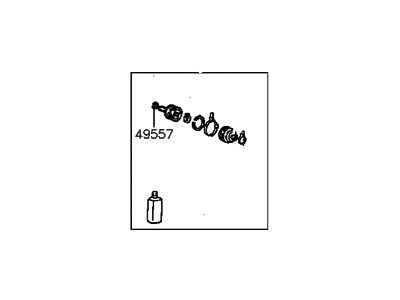
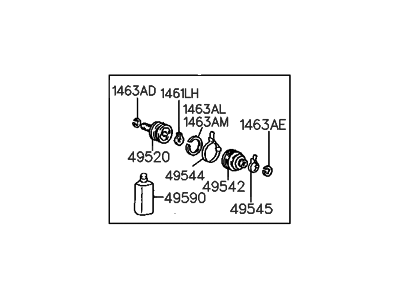
Genuine Hyundai Elantra CV Joint Boot
Constant-Velocity Joint Boot- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
93 CV Joint Boots found
Hyundai Elantra Boot Kit-Front Axle Differential Side
Part Number: 49506-2HA31$54.61 MSRP: $76.06You Save: $21.45 (29%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysHyundai Elantra Joint Kit-Front Axle Differential Side
Part Number: 49535-F2305$232.52 MSRP: $326.68You Save: $94.16 (29%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysHyundai Elantra Boot Kit-Front Axle Differential Side
Part Number: 49542-F2105$43.45 MSRP: $60.52You Save: $17.07 (29%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysHyundai Elantra Boot Kit-Front Axle Differential Side
Part Number: 49542-F2305$43.45 MSRP: $60.52You Save: $17.07 (29%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysHyundai Elantra Joint Kit-Front Axle Differential Side RH
Part Number: 49535-F2200$198.67 MSRP: $279.13You Save: $80.46 (29%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysHyundai Elantra Joint Kit-Front Axle Differential Side
Part Number: 49505-28A00$205.73 MSRP: $289.05You Save: $83.32 (29%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysHyundai Elantra Joint Kit-Front Axle Differential Side RH
Part Number: 49582-3Y150$343.67 MSRP: $482.84You Save: $139.17 (29%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysHyundai Elantra Joint Kit-Front Axle Differential Side LH
Part Number: 49592-3X2A5$275.77 MSRP: $387.45You Save: $111.68 (29%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysHyundai Elantra Joint Kit-Front Axle Differential Side LH
Part Number: 49582-3Y100$330.31 MSRP: $464.08You Save: $133.77 (29%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysHyundai Elantra Boot Kit-Front Axle Wheel Side RH
Part Number: 49609-29L00$13.30 MSRP: $17.19You Save: $3.89 (23%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysHyundai Elantra Boot Kit-Front Axle Differential Side
Part Number: 49542-F2205$43.45 MSRP: $60.52You Save: $17.07 (29%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysHyundai Elantra Boot Kit-Front Axle Wheel Side LH
Part Number: 49509-29L00$54.58 MSRP: $76.02You Save: $21.44 (29%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysHyundai Elantra Joint Kit-Front Axle Differential Side
Part Number: 49505-2CH00$184.40 MSRP: $259.08You Save: $74.68 (29%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysHyundai Elantra Joint Kit-Front Axle Differential Side RH
Part Number: 49535-F2300$202.25 MSRP: $284.16You Save: $81.91 (29%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysHyundai Elantra Joint Kit-Front Axle Differential Side
Part Number: 49505-28E00$205.73 MSRP: $289.05You Save: $83.32 (29%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysHyundai Elantra Joint Kit-Front Axle Differential Side
Part Number: 49505-28E01$205.73 MSRP: $289.05You Save: $83.32 (29%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysHyundai Elantra Joint Kit-Front Axle Differential Side
Part Number: 49505-29L00$205.73 MSRP: $289.05You Save: $83.32 (29%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysHyundai Elantra Joint Kit-Front Axle Differential Side
Part Number: 49505-33A10$205.73 MSRP: $289.05You Save: $83.32 (29%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysHyundai Elantra Joint Kit-Front Axle Differential Side
Part Number: 49505-2DE00$219.68 MSRP: $308.65You Save: $88.97 (29%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysHyundai Elantra Joint Kit-Front Axle Differential Side LH
Part Number: 49505-29J00$219.91 MSRP: $308.97You Save: $89.06 (29%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
| Page 1 of 5 |Next >
1-20 of 93 Results
Hyundai Elantra CV Joint Boot
If you are looking for affordable high-quality OEM Hyundai Elantra CV Joint Boot, then you have come to the prime place. Our website provides a large amount of genuine Hyundai Elantra CV Joint Boot at unbeatable prices. All our parts come backed with the manufacturer's warranty.
Hyundai Elantra CV Joint Boot Parts Questions & Experts Answers
- Q: How Should You Check the CV Joint Boot and Shock Absorbers on Hyundai Elantra?A:Tire wear, poor ride quality, reduced fuel economy, and compromised vehicle handling may be caused by worn or damaged components in the steering linkage and suspension. To examine the shock absorbers, stop the engine when your vehicle is on level ground and engage the parking brake. You should push down on each corner of your vehicle to see if it stops moving and returns to a level position within one or two bounces. This could be a result of weak or worn-out shock absorbers if the vehicle continues to move or fails to return to its original position. Raise the vehicle and inspect the shock absorbers for fluid leakage; ensuring they are firmly mounted as well as undamaged. Furthermore, check visually for damage, leaks, and wear on steering as well as suspension components. Inspect the lower control arm, stabilizer bar connections, tie rod ends, and ball joints for damage or movement signs respectively. Finally, ensure CV joint boots are free from any tears, cracks, or loose clamps that would allow dirt or water to enter, damaging the CV joints.
Related Hyundai Elantra Parts
Browse by Year
2023 CV Joint Boot 2022 CV Joint Boot 2021 CV Joint Boot 2020 CV Joint Boot 2019 CV Joint Boot 2018 CV Joint Boot 2017 CV Joint Boot 2016 CV Joint Boot 2015 CV Joint Boot 2014 CV Joint Boot 2013 CV Joint Boot 2012 CV Joint Boot 2011 CV Joint Boot 2010 CV Joint Boot 2009 CV Joint Boot 2008 CV Joint Boot 2007 CV Joint Boot 2006 CV Joint Boot 2005 CV Joint Boot 2004 CV Joint Boot 2003 CV Joint Boot 2002 CV Joint Boot 2001 CV Joint Boot 2000 CV Joint Boot 1999 CV Joint Boot 1998 CV Joint Boot 1997 CV Joint Boot 1996 CV Joint Boot 1995 CV Joint Boot 1994 CV Joint Boot 1993 CV Joint Boot 1992 CV Joint Boot 1991 CV Joint Boot